SEO for SaaS: The Definitive Guide for 2026
Ranking on Google is difficult right now. Your material should appear everywhere, including on AI-powered platforms such as ChatGPT and Perplexity, as well as in conversations on Reddit and LinkedIn. Why? Because the software as a service market has exploded. It is currently worth more than $250 billion and continues to grow, with new cloud-based solutions being introduced every week.

Your competitors are competing for the same customers you want to attract. As a result, you’re trying to grasp SEO for SaaS companies. In this definitive SaaS SEO guide, we explain SaaS-specific strategy concepts that enable us to market to the right users.
What Is SaaS SEO?
This is the practice of optimizing the SaaS website to improve its exposure and rankings in a search engine such as Google and Bing. To increase rankings, prospects, and clients interested in the software solution your SaaS business provides.
A process entails adopting several SEO tactics, including keyword analysis, technical SEO (optimizing your site for organic search and user experience), and link building (acquiring links that refer to the site), and necessitates a SaaS-specific strategy.
Best SaaS SEO Strategies in 2026
B2B SaaS SEO will continue to be a key growth driver in 2026 since it compensates for increased client acquisition costs. Unlike sponsored channels, where costs rise linearly with demand, having comprehensive SaaS SEO strategies guarantees long-term demand capture by aligning your content with user intent throughout each funnel touchpoint.
One would prioritize high-intent use cases, integrations, and problem-aware queries to ensure organic traffic is conversion-ready. We use product-driven content, solid technical underpinnings, and AI-powered optimization. Search algorithms prefer unambiguous entity positioning, genuine product expertise, and trust signals to generic content volume.
Keyword Research for SaaS
SaaS keyword research is the process of identifying relevant keywords that your target audience uses on Google to find your product or the problem it solves. You must constantly iterate, and this is not restricted to commercial or branded keywords.
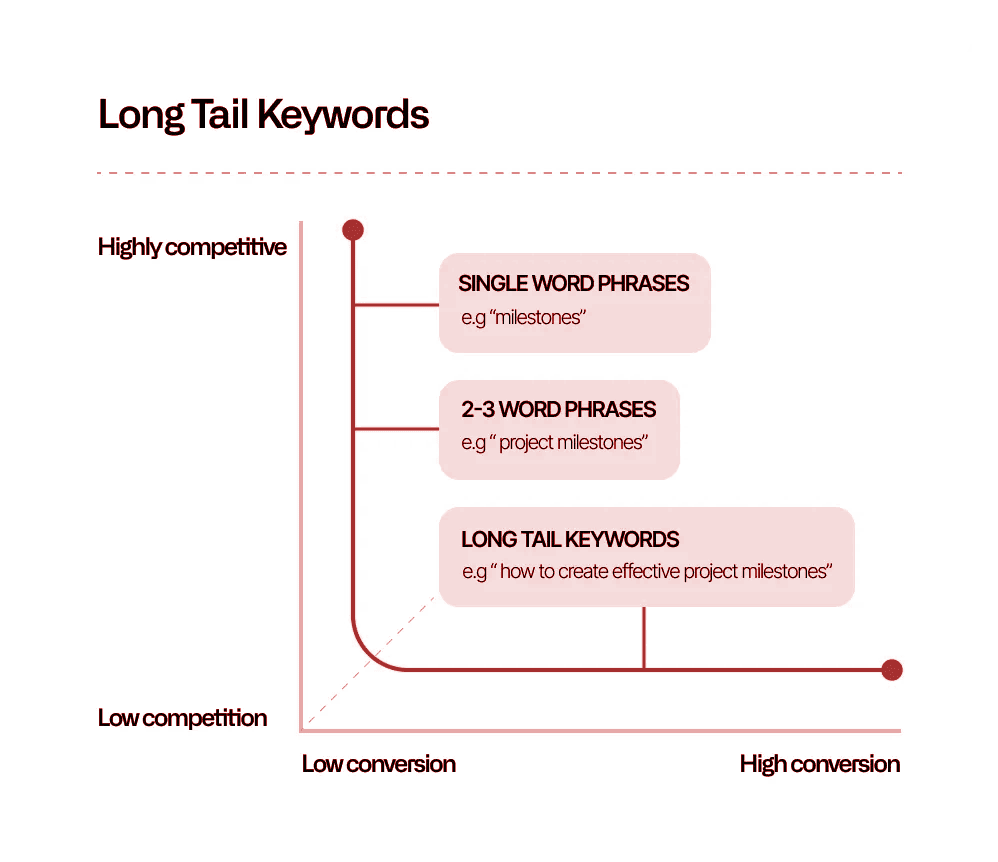
Let’s take Mailchimp’s email automation product. The organization cannot solely develop material for keywords such as “Mailchimp features.” They must also write content for keywords such as “best email automation tools” and “what is email automation.” These searches allow you to attract targeted traffic to your website and convert visitors into free trial sign-ups using actionable CTAs.
Identifying JTBD Keywords
JTBD keyword research connects search queries to the underlying functional, emotional, or operational “job” that the user is attempting to fulfill. Rather than focusing on product names, it looks for problem-aware language like procedures, limitations, or results. These keywords usually show early in the funnel, necessitating intent modeling, SERP analysis, and use-case clustering.
BOFU Keywords for SaaS Companies
BOFU keywords indicate high purchasing intent and are intimately related to the assessment and decision stages. They include branded terms, competition comparisons, pricing inquiries, implementation information, and feature-specific searches. Effective SaaS business BOFU research prioritises minimum ambiguity, commercial modifiers, and alignment with sales enablement assets such as demos, trials, and use cases.
AI-Driven Keyword Research
AI-driven keyword research uses machine learning algorithms to detect patterns in massive datasets, such as semantic similarities, intent shifts, and emerging demand.
It goes beyond static volume data to estimate keyword value using conversion likelihood, SERP volatility, and topical authority gaps. This method allows for scalable clustering and ongoing optimization.
Product-Led SEO Strategies for SaaS Brands
Product-led SEO is the idea of creating a valuable product just for people. Your SaaS business isn’t posting content because a keyword tool instructs it to, but rather to create a story about a product that customers want. The difference is that you’re generating a product description that helps consumers decide whether or not to buy, rather than a keyword-rich description.
When developing a product, you begin with SaaS SEO strategies to assist your organization in targeting a specific topic. How does the content you create relate to the rest of your inputs? Learn about what people want, what they’re seeking, and their basic expectations.
Mapping Product Features to User Jobs-to-Be-Done
This content strategy converts product capabilities into search demand by matching features to the specific jobs that users are attempting to fulfill.
Keyword targeting is focused on operational duties, restrictions, and desired outcomes, not feature labels. This enhances intent alignment, minimizes mismatch traffic, and boosts relevance for both problem-aware and solution-aware searches.
Bottom of the Funnel Content for High Intent
BOFU material is geared toward evaluation-stage searches, in which users are actively comparing options or planning to purchase.

This covers pricing logic, competitor comparisons, integrations, migrations, and implementation specifications. These assets directly impact revenue by eliminating uncertainty, verifying fit, and facilitating sales-assisted or product-led conversion routes.
Demos and Trials in SEO Content
Embedding demos and free trials on SEO pages ties organic demand to end-user product usage.
Content is intended to guide visitors from validation to hands-on experience with little friction. This boosts product-qualified leads, improves engagement signals, and aligns SEO performance with product-driven growth and revenue targets.
Programmatic SEO for SaaS Companies
Programmatic SEO is the process of creating hundreds or thousands of optimized landing pages for specified, frequently long-tail keywords utilizing automation, templates, and structured data.
Instead of manually developing each page, you create a template and dynamically populate it with data. The programmatic approach is especially effective for SaaS enterprises because your product likely serves diverse use cases, integrates with various technologies, targets different industries, or addresses problems in a variety of circumstances.
Scaling Pages for Integrations and Use Cases
This method (continued acceleration) uses structured templates to programmatically scale pages for product integrations and core use cases while preserving intent specificity. Each site focuses on a specific process or tool pairing, with standardized metadata, internal linking, and unique contextual copy to avoid duplication and maintain relevance at scale.
Optimizing Vs Comparison Pages
Comparison pages are designed to address high-intent evaluation queries in which users choose between alternatives. Effective optimization considers feature parity, use-case fit, pricing tradeoffs, and implementation complexity. Neutral framing, clear difference, and trust signals boost conversion rates while strengthening topical authority for competing commercial terms.
Automation Tools
Automation technologies are used to simplify research, clustering, internal linking, and performance monitoring, rather than to replace strategic input. In a crowded industry, automated SEO for SaaS companies promotes scale and consistency but must be limited by human monitoring to ensure EEAT, intent accuracy, and long-term ranking stability.
Technical SEO for SaaS Businesses
Technical SEO focuses on optimizing your website’s technical characteristics to ensure that it meets the key standards of Google and improves organic rankings. Crawling, rendering, indexing, and website architecture are the four search characteristics that are prioritized in technical iteration. When you focus on these characteristics, you make your site crawlable. This means a search engine can easily crawl your website and index all of its key pages.
Core Web Vitals with INP Focus
Optimizing INP (Interaction to Next Paint) necessitates less main-thread blocking during user interactions. SEO for SaaS websites involves postponing non-critical JavaScript. It’s about breaking down large operations into smaller bits, and prioritizing event handlers related to navigation, filters, and CTAs. Framework-level optimizations (e.g., React hydration control, selective rendering) and real-user monitoring through CrUX are crucial.
Clean Site Architecture
A clean architecture ensures logical hierarchy and crawl efficiency. Pages on SaaS sites should be organized by intent (for example, features, use cases, integrations, and comparisons) and have a shallow depth and consistent URL structure. Strong internal linking between related commercial pages distributes authority, enhances indexing, and clarifies topical relationships to search algorithms.
Implementing SoftwareApplication Schema
The SoftwareApplication schema should be used on core product pages to specifically identify category, pricing model, operating system, and application type.
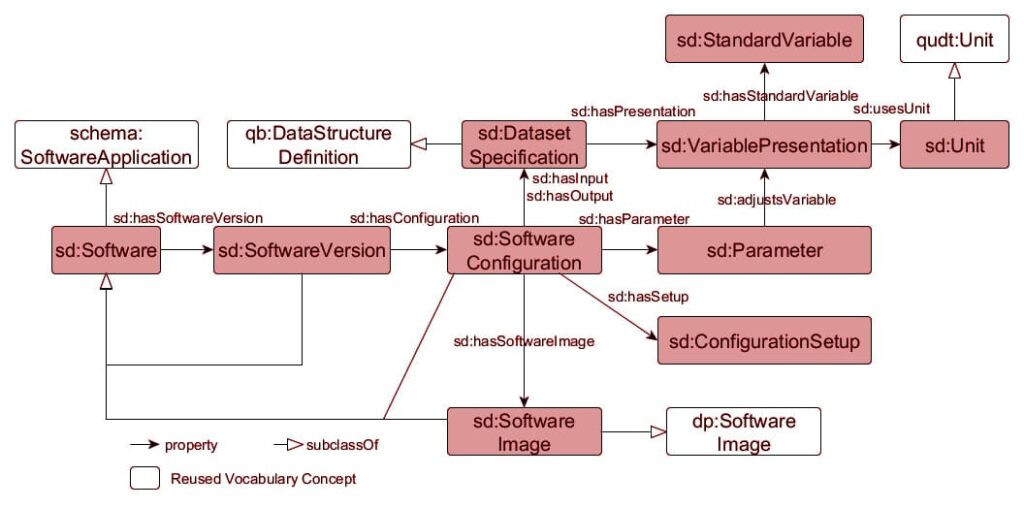
Structured data must reflect real product attributes and be consistent with on-page content. When properly linked with reviews and FAQs, schema increases eligibility for improved SERP features and enhances entity recognition.
Mobile and Speed Optimization
Mobile optimization prioritizes performance in restricted environments. SaaS teams should use mobile-first design, avoid layout changes, compress assets, and use CDN caching.

Reduced JavaScript payloads, optimized fonts, and fewer third-party scripts all contribute to faster crawl efficiency, engagement metrics, and conversion rates.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO focuses on improving individual web pages so that they rank higher and receive more relevant traffic. It customizes methods to meet the unique needs of SaaS enterprises, which can have complex sales cycles and various client touchpoints.
Unhelpful information recycles details without providing a new perspective or depth. Key components of SaaS on-page optimization include keyword identification, quality content production, technical SEO, and UX improvements. This includes optimizing page metadata, headers, and graphics, as well as ensuring fast loading times and mobile responsiveness.
Titles, Meta Descriptions, and Headers
Crawlers interpret titles and headers as signals of primary intent and keyword hierarchy. Meta descriptions, on the other hand, have an impact on SERP click-through without directly affecting rank.

Better intent signaling and better CTRs boost impressions-to-click conversion, which feeds behavioral signals (CTR, dwell) that support enhanced ranking and traffic.
Strategic Keyword Integration
The proper placement of primary and secondary keywords connects pages with various user intents and topical groupings. This raises the number of queries a page may rank for, enhances relevance scores, and boosts qualified organic impressions.
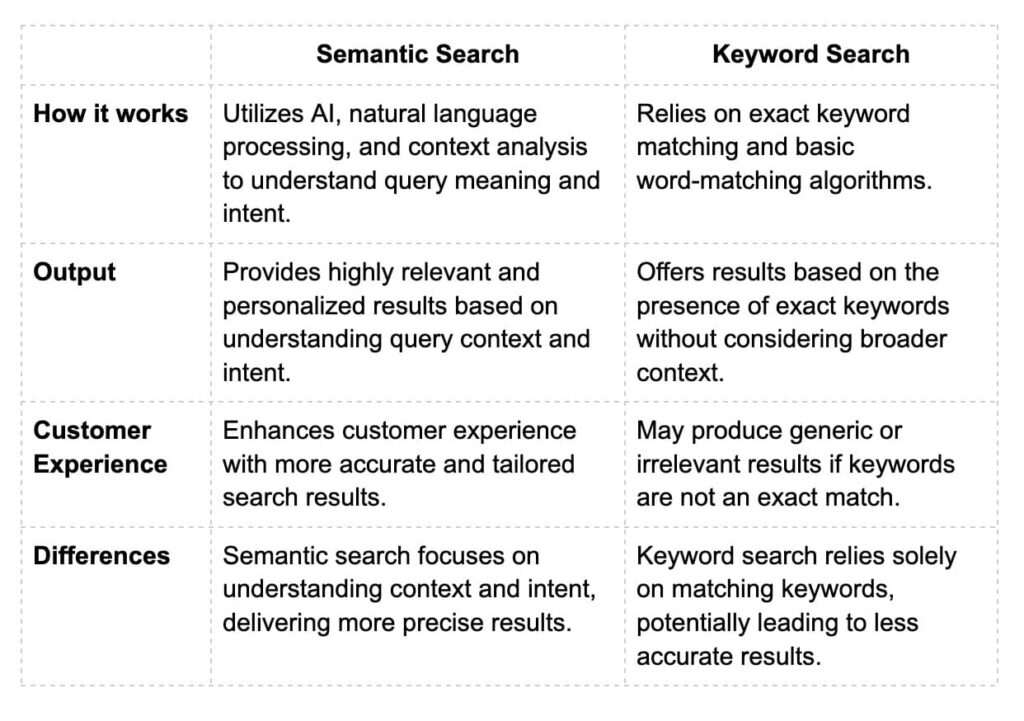
A semantic keyword promotes long-tail exposure, allowing pages to attract visitors beyond their original target phrase.
Internal Linking
Internal connections convey crawl equity and clarify entity relationships across pages, resulting in faster indexing of priority information. Targeted linking increases the ranking potential of commercial pages while also increasing organic session depth and pages-per-session, both of which correspond with increased conversion yield. Internal links that are strategically placed direct crawlers and users to high-value pages, hence enhancing crawl prioritization and assisting conversions.
Optimizing Multimedia for User Engagement
The images and videos that have been properly optimized minimize load, improve comprehension, and increase time on page and scroll depth. Strong engagement signals reduce pogo-sticking and bounce rates, indirectly enhancing rankings and organic visitor retention. Multimedia allows for image and video SERP features, which increases surface-level visibility.
Interactive Content and Lead Magnets
Organic visitors are converted into product-qualified leads with interactive tools and gated assets, which also increase time-on-site and repeat visits. Though they are not direct ranking considerations, they increase behavioral metrics and lifetime value per organic visitor, making SEO expenditures more revenue-generating. These assets boost repeat visits and brand remember, which increases the possibility of future branded searches and assisted organic conversions.
Trust Signals Integration
Third-party evaluations, case studies, certificates, and author credentials boost perceived authority while lowering purchasing friction. These signals increase organic traffic conversion rates while also improving long-term ranking resilience by strengthening EEAT and referral-driven sponsored demand. Trust indicators further reduce hesitancy during the evaluation process, increasing the conversion efficiency of high-intent organic sessions.
AI Search
SEO tools like ChatGPT and Gemini generate information about your software right in their interfaces. When someone asks, “What’s the best email marketing platform for ecommerce?” they frequently receive a detailed response without ever visiting the website.
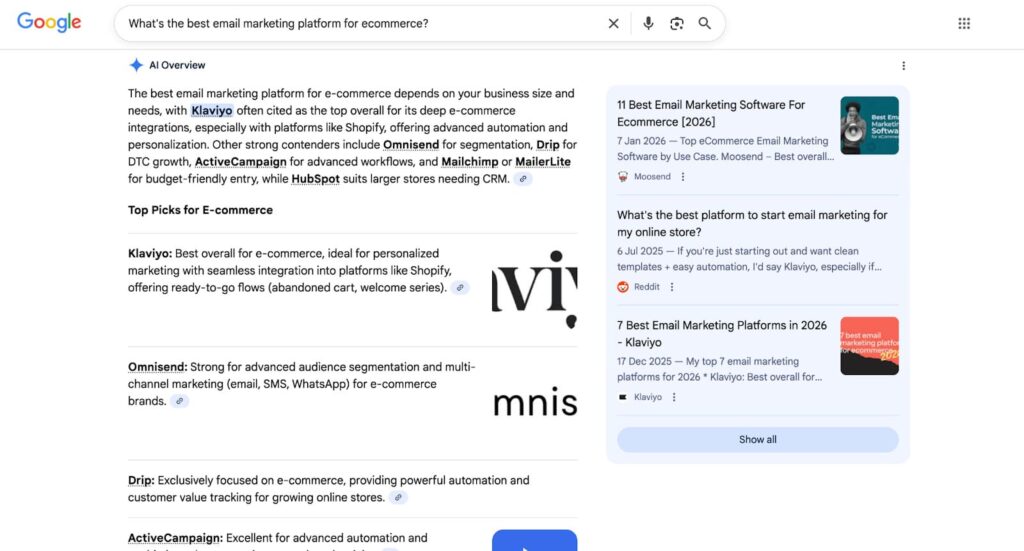
AI collects and references specific paragraphs regarding your SaaS product features, pricing, integrations, and benefits. Every content asset or variable on the website, from feature descriptions to help articles, must be self-contained and structured for AI understanding.
Getting Cited in AI Overviews
AI Overviews prioritize content by providing explicit entity definitions, authoritative sourcing, and succinct responses that address user intent early on the page. SaaS sites boost citation likelihood by arranging information with specific assertions, supporting evidence, and scannable summaries that follow the retrieval and attribution patterns utilized by large language models.
Generative Engine Optimization for SaaS
Generative Engine Optimization, as we call it, aims to make SaaS information retrievable, interpretable, and quotable by an LLM-based search engine. This includes strong topical authority, standardized terminology, structured data, and first-hand knowledge that models may rely on when answering commercial or technical questions.
Structuring Content for AI and Featured Snippets
Clear headings, direct answer blocks, orderly lists, and definition-style paragraphs are all used in AI and snippets-ready content.
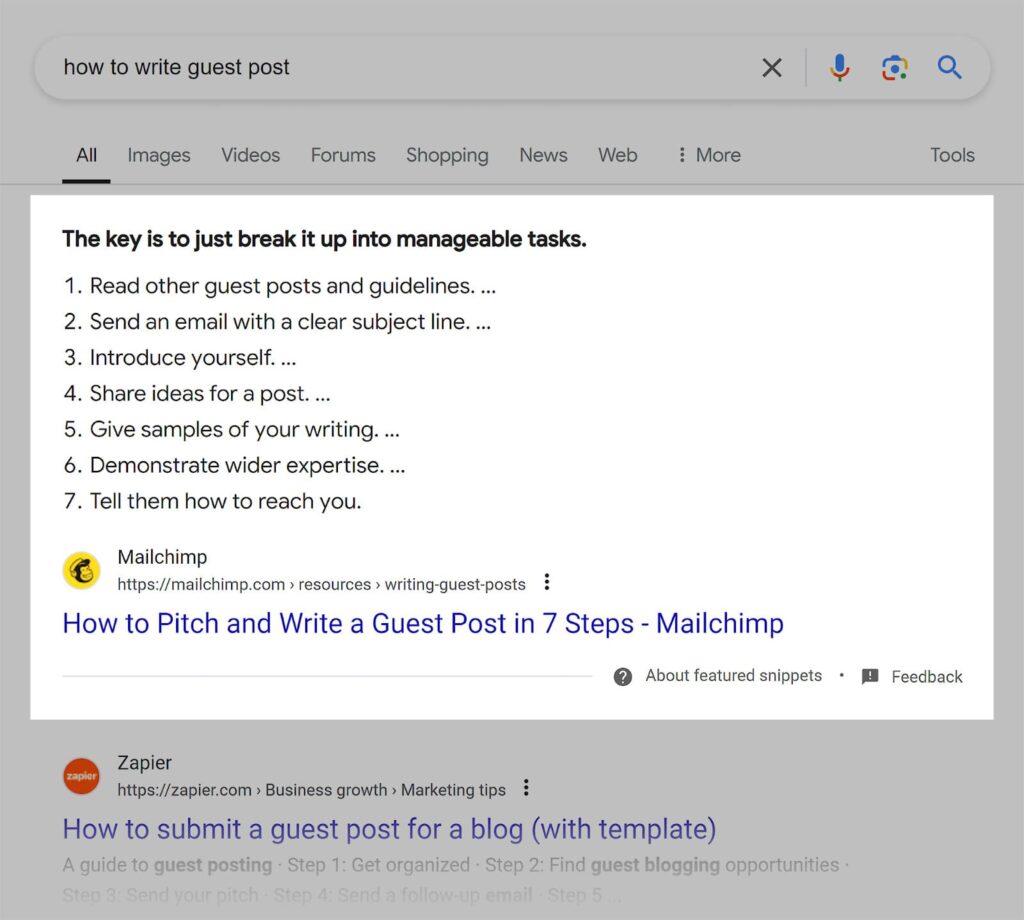
For B2B SaaS companies, this entails prioritizing explanations, explicitly defining concepts, and reducing ambiguity so that search algorithms and generative systems can extract precise, high-confidence responses.
The Human-AI Content Loop
When most people hear the term “human-in-the-loop,” they envision AI as a productivity booster. Smart tools that make work simpler, faster, and more efficient. That isn’t inaccurate, but it is incomplete.
In SaaS marketing, human-in-the-loop refers to an execution paradigm in which AI manages production while humans take content strategy, quality control, expertise, and judgment. Rather than selecting between AI automation and human execution, person-in-the-loop blends the two. Using AI for its strengths and humans for theirs (creativity, knowledge, and nuance).
Scaling Content with AI
The human-AI content loop employs AI to scale research, outlines, initial drafts, and content variation across massive SaaS keyword sets. This allows for coverage of long-tail, integration, and use-case queries while retaining structural consistency. AI improves throughput, but output is limited by specified intent models and content standards.
Maintaining E-E-A-T with Real Data & Experts
E-E-A-T is preserved by grounding AI-generated content in proprietary data, product telemetry, consumer insights, and subject-matter experts.
Human contributions confirm assertions, inject lived experience, and contribute novel analysis that AI cannot develop on its own. This promotes credibility, distinction, and robustness to quality-based ranking erosion.
Human Oversight for AI Content
A human monitoring ensures accuracy, intent alignment, tone, and adherence to brand and search quality criteria. Editors check AI output for hallucinations, unsupported assertions, and general phrasing to ensure each page provides verifiable value. This control layer guards against scale-induced quality erosion and ensures long-term organic performance.
Conversion-Focused Link Building
A practice that falls into off-page SEO, conversion-focused link building, views links as both traffic and revenue channels. High-quality, contextually relevant backlinks pass authority while exposing SaaS pages in front of qualified audiences, increasing the likelihood of organic visibility and conversion.
One would value links from authoritative, niche-aligned sources since they increase trust, enhance rankings for commercial queries, and offer referral traffic that fits buyer intent. Effective link-building techniques include link-worthy SEO efforts, selective guest authoring, broken-link replacement, and brand-mention reclamation, all of which are judged by referral quality, assisted conversions, and revenue effect rather than link numbers.
International SaaS SEO
International SEO is the practice of optimizing the website to increase traffic from foreign markets. It consists of two main components: organizing your website so that the target search engine understands which nations you are targeting and localizing content to match your audience’s keywords.
For example, a SaaS product that provides project management solutions can enter the German market by optimizing its website and generating localized material about time tracking and efficiency. Without international SEO, the product may stay inaccessible to German consumers who are actively looking for solutions adapted to their work culture and language preferences.
Geo-Targeting for Global Growth
Geo-targeting ensures that content for subscription-based products is presented to the appropriate regional audience using hreflang tags, ccTLDs, or subfolders. Accurate configuration eliminates duplicate content issues, enhances SERP relevance by market, and signals to Google which version should rank for each region, allowing for scalable international organic development.
Multilingual SEO
Multilingual SEO entails developing fully indexed, language-specific pages that include appropriate HTML language tags, metadata, and canonicalization. For cloud-based product suppliers, prioritizing multilingualism increases search exposure in non-English markets while preserving crawl efficiency and preventing authority dilution across various languages.
Localization vs Translation
Localization tailors information to the cultural context, currency, units, and regional terminology, whereas translating is a direct linguistic conversion. True localization enhances engagement, bounce rates, and conversion rates for SaaS brands while signaling importance to crawlers and indexing bots in each target area.
Region-Specific Keyword Research
Conduct keyword discovery by area, taking into account market share, colloquialisms, query modifiers, and SERP feature popularity. Normalize volume and CPC data across tools, analyze seasonality and intent volatility, and associate term clusters with local landing sites. Competitive gap research versus regional incumbents guides content prioritization and go-to-market sequencing.
Local Trust Signals
Create region-specific credibility with local case studies, integrations with prominent local platforms, localized reviews, and regulatory or compliance badges. Provide regional support channels, payment methods, and transparent data residency disclosures. Mark reliable SEO efforts with schema and obtain third-party endorsements to convert high-intent local searchers.

Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it typically take to see a positive ROI from SaaS SEO?
SaaS SEO ROI typically ranges between 6 and 12 months, depending on niche competitiveness, content velocity, and product-market fit. Long-tail and use-case inquiries frequently outperform high-intent commercial keywords in terms of quantitative conversions.
How to choose the right keywords for a niche SaaS?
Instead of generic volume data, an SaaS SEO agency would focus on keywords that match user Jobs-to-Be-Done, feature-specific workflows, and the intent stage. Combine competition analysis, SERP intent evaluation, and semantic clustering to find the phrases that drive qualified traffic and conversions.
How often should old SaaS content be updated to maintain search rankings?
Like in traditional SEO, high-value SaaS pages should be evaluated at least once every 6-12 months to ensure correctness, feature updates, and market changes. Updates should provide new technical information, integrations, price, and outcomes to maintain relevance and EEAT signals.
Is SEO still worth it for SaaS in 2026?
Organic search is still the major acquisition method for high-intent B2B audiences, particularly for scalable and evergreen content such as use cases, integrations, and BOFU assets. The emphasis has shifted to human-authored, trust-driven SaaS SEO content strategy, which AI cannot copy, hence increasing long-term visibility and conversions.





