Technical SEO for Ecommerce
Getting those products in front of your potential clients is the first step in ecommerce SEO. You must make sure that products and information are discoverable if you wish to use Google for that.

Technical SEO can help with this. By combining your goals with the best ecommerce SEO strategies we’ll go over in this post, you may increase the likelihood that the products will appear on Google and improve user experience by relying on usability and load speed.
What Is Technical SEO?
The process of making sure a website satisfies the technical standards of Google to optimize ranks. Website structure, crawling, indexing, and rendering are components of technical SEO. They inform search engines, such as Google or Bing, about the connections between the pages when they’re optimized. A page experience might be a competition breaker; it’s crucial for your ecommerce business.
How It Differs from On-Page and Off-Page SEO
In summary, technical SEO ensures that the website’s code is clear and efficient, off-page SEO involves gaining some link juice to increase domain authority, and on-page SEO focuses on optimizing the website for both users and search engines.
While each type is critical, if you want to begin gradually with SEO, we advise starting with on-page, then moving on to its technical assets, and finally honing the off-page optimization.
Why Technical SEO important for an Ecommerce Business
The value of your content is rendered meaningless when a search engine is unable to access the site. The reason for this is that the website will not show up in search results. It’s valid for online stores with a lot of pages, including products and categories.

It’s important since it also secures a property’s user-first purpose. To draw in organic traffic and convert those visitors into paying clients, you’ll need solid technical optimization.
How Search Engines Index Ecommerce Sites
A product catalog must be processed for the ecommerce site to work correctly. Every product is examined and its specs, including category, price, title, and description. The engine can get your content thanks to the process of classification.
Google uses crawlers to download all the materials from websites. After that, it examines the materials and enters the data into the index database. When a person searches, the search engine provides them with relevant results.
Optimizing Site Architecture for Ecommerce SEO
A reasonable site architecture is orderly and user-friendly. You’ll frequently see categories with subcategories beneath them on a website with the same architecture. Since e-stores feature more pages than other websites, it’s crucial to think about how to make the site architecture as user-friendly as possible. Besides saving you time in the future, it’ll give the website visitors a great experience, which will result in ecommerce SEO success.
How Site Architecture Affects SEO
Though it takes effort to optimize your architecture, the benefits outweigh the drawbacks. An organized website improves ecommerce SEO by making it simpler for Google algorithms to index and rank the pages. More organic traffic and greater visibility result from this.
With an optimal architecture, users are more engaged, and bounce rates are lower when they discover what they need. Consider future-proofing the online stores to ensure they stay friendly with both Google and its users.
Preventing Duplicate Content Issues
Redirects can be used to link a couple of pages into a single, referenceable content version. You should set 301 redirects from non-preferred URLs to your desired one. These redirects inform algorithms, which index, that your material has been redirected to another URL.
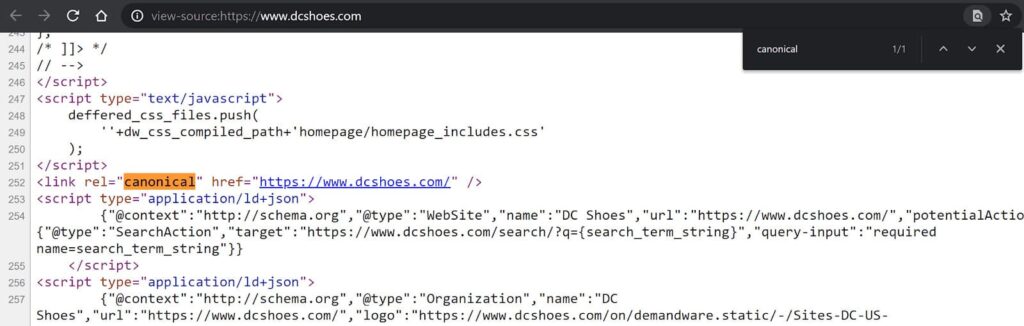
Use canonical tags to eliminate duplicate content: in the <head> section of HTML codes, include the <link rel=”canonical” href=”URL”> tag. It informs search engines of the best version of a page to index and display in results. Canonical tags indicate to search engines which version of a page is preferred for appropriate ranking evaluation.
URL Optimization
In SERPs, a clean URL encourages users to click on the link. Ranking potential is raised when your URLs are scannable. When your URL reflects the topic and purpose of a page, it becomes more accessible for search engines to get the kind of content you have there.
A shorter URL is simpler to remember and distribute. Try to find URLs that are brief but informative.
Example: example.com/buying-guide
Don’t use terms like “and,” “of,” and “the.” Use only the most important words that express the purpose.
Optimizing Category Pages and Product Pages
While product pages concentrate on particular items with their specs, categories target more general terms and act as a gateway to products.
As product pages need clear images, extensive content, and conversion-focused elements, such as reviews and CTAs, optimizing category pages entails improving navigation, and internal linking.
Internal Linking Strategies for Better Indexing
A page may not even appear in search results if it has no links. Prioritize linking to the most valuable pages first; these could be content, service, or category pages. Including links to them improves their SEO rankings and visibility. There should be more internal links on your pages to index them.
How to Optimize Category Pages for Target Keywords
Performing keyword research is the first step in improving your category page. You can precisely match user intent by focusing on long-tail terms. You can accomplish this using free tools for keyword research, but hiring an outside firm with the know-how to target keywords for ecommerce business needs is going to drive greater results.
On-Page Optimization
The term on-page SEO describes actions that can be made within a website to raise its position. Examples of this include enhancing the title tags and metadata or optimizing the content relying on ecommerce keyword research. Therefore, analysis and ongoing monitoring are two essential components to put in place if you want to optimize the performance systematically.
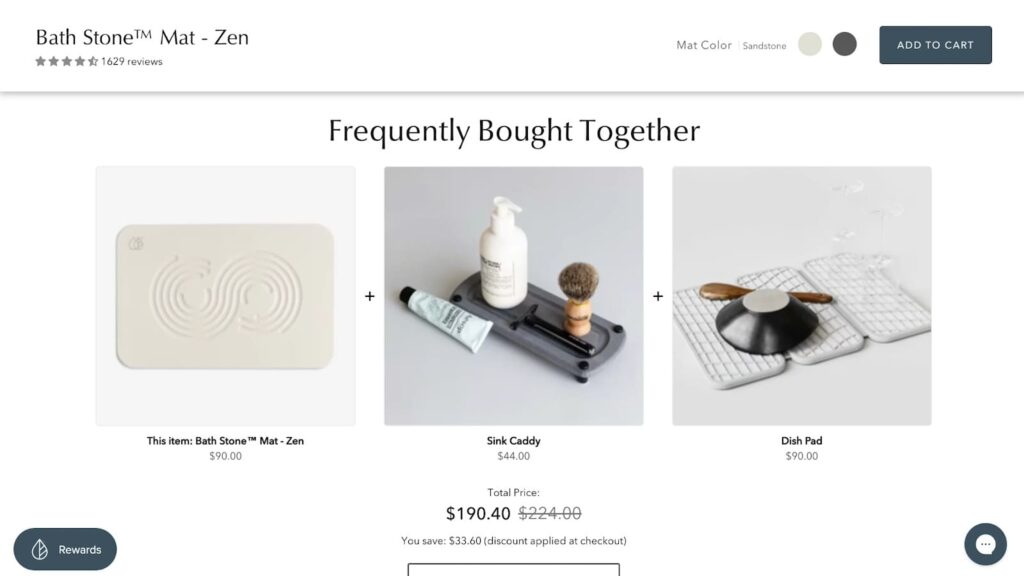
Optimizing Product Page Content
Provide the model number, product name, brand name, and the SKU. Your product name, metadata, and URL must all contain a target keyword.
Each product page should be optimized for product-specific keywords, not for brand or brand and product category keywords, as you don’t want product pages to compete with your category page.
Writing Engaging Product Descriptions
Well-written product descriptions persuade users to purchase from you. Don’t write an essay, but make them personal and describe the advantages.
Besides describing the product, when ecommerce keyword research is done, it’s important to list its specifications, such as weight, color, and size: everything a visitor would be looking for on Google to complete a purchase.
Using High-Quality Images and Alt Text
Conversion is likely to increase when clear photos of the products are included. So, you can display a person in a themed setting with a product.
An option for search engines is provided by an alt tag, which is an HTML property appended to the images. Adding product photographs to alt tags might improve your position in search.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
This data makes it easier for Google algorithms to comprehend the content of the website. You must give succinct details about the page and what’s featured here. Data structuring makes it easier for crawlers to properly classify the content on a particular page, thereby increasing its visibility in search results.
What is Structured Data?
A framework for describing a page and categorizing its content is called structured data. Schema is a particular kind of data that gives the content on your page context and meaning. It’s a method of classifying data so that Google may access and process it.
Implementing Schema Markup
The microdata must be added to the HTML code to apply schema markup to a website. A developer can accomplish this manually, or a Data Markup Helper can automate it. For example, an ecommerce website may be more likely to show up in results for the featured product-related inquiries if it has a product schema.
Internal Linking Strategies
To let Google know that this is the main content, you need to include a lot of internal links. You must contextualize your buying guides when you write them. It’ll demonstrate to Google how thematically connected the content is. You’ll include links after your post or include links within sentences.
Improving Indexability and Crawlability
The ecommerce SEO industry misunderstands the distinction between crawling and indexing. When a Googlebot crawls a page, it examines all of the code on the page. When a page is scannable for Google algorithms, it can appear in SERP.

Your site’s crawlability and indexability will greatly benefit from frequent updates and relevant content. Google values material that is user-centric. It indicates that an ecommerce site is active since you added fresh content and updated it.
Optimizing Your Sitemap and Robots.txt
To guarantee that the content is correctly processed by Google Search Console, this file should always be prepared, regardless of the site’s size. You don’t need an HTML sitemap unless you have 10k+ pages. It’s not as critical to algorithms as an XML, but if it’s reasonable, it may help users who find it.
Optimizing crawl spending and an ecommerce SEO requires the strategic use of a robots.txt file. To have Googlebot not index the bottom-line pages, for example, you should configure the robots.txt files since they block access for the bots.
Enhancing Site Speed and Performance
The fundamental principle of technical SEO is a responsive ecommerce website. Using a content delivery network (CDN) and resizing photos are two strategies to help increase its speed. Caching content across servers is how a CDN operates.
Static assets like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are render-blocking resources. The algorithm stops downloading other resources until these files are processed. Reducing them helps you cut down on the rendering time and speed up page loads.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
To help Google show accurate information about the products through Google Maps apply a sitemap. For Google Shopping and Google Images, product data is supplied with Google Merchant Center. This way, the click-through rate (CTR) can be increased.
For pages that have an HTML <script> tag wrapped around them, you can locate schema. The script-type application ID is contained in the script tag.
Rich Snippets and Their Impact on Click-Through Rates
Google creates rich snippets to feature extra details, such as reviews and delivery, using schema. Rich snippets improve the appeal of your ranks, which can increase click-through rates. A user is more likely to notice a result with a product image than one with plain text.
Ecommerce products benefit from them. The user might interact with the product snippet if it grabs their interest, which would result in a transaction.
Implementing Schema Markup
Choose the format for your page’s schema first. Google recommends JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) because it is simple to use and maintain. RDFa and Microdata, which are linked straight to the HTML code, are other options.
Product Schema for Product Pages
You can include important information about your products, even availability, using a Product Schema Markup.
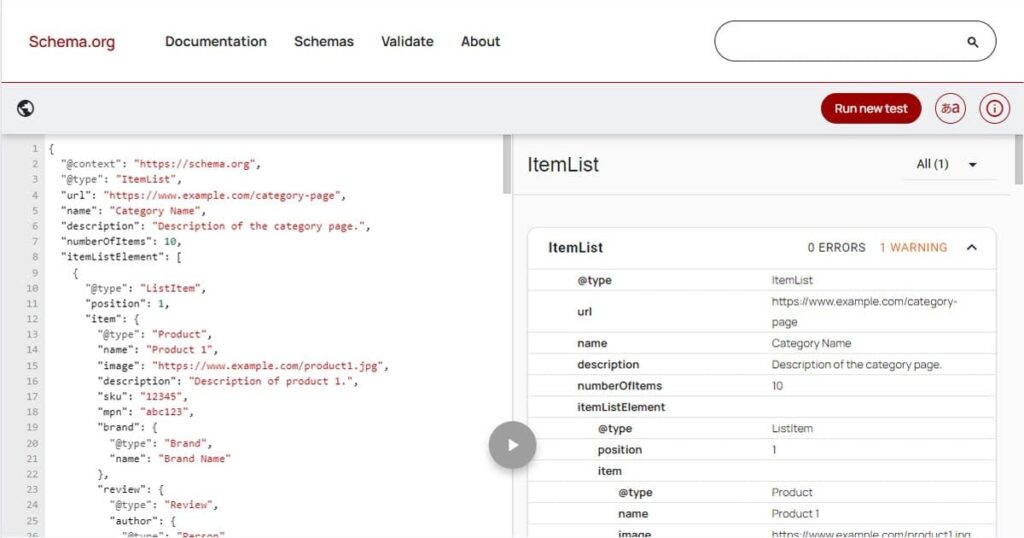
Google can comprehend the details of your offerings and present them prominently in search intent thanks to the data you organize.
Review Schema for Customer Ratings
Ratings and reviews are strong forms of social evidence that can sway judgments about what to buy. The products gain the trust of prospects.

Users are more inclined to browse product pages and place an order when they find customer reviews.
Breadcrumb Schema
The type of schema specifying the crumb trail on a webpage is called a breadcrumb list schema.
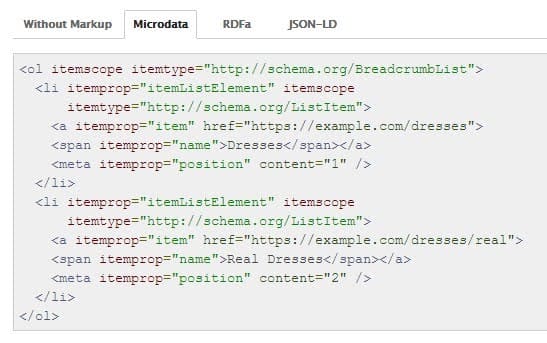
You’ll tell Google the trail by using this schema, which helps them understand how the present page fits into the overall structure of any ecommerce site.
Technical SEO for Mobile and User Experience
If you wish to get organic traffic, you must prioritize mobile technical SEO. It provides a user experience for those who use touchscreens. Mobile device users can access the pages due to optimization. Then, your ecommerce SEO will be in line with mobile-first crawling.

A mobile-friendly ecommerce site must have a few elements; consisting of usability, touch-friendly navigation, and responsive web design. These all have an impact on SEO and UX performance.
Google’s Mobile-First Indexing and Its Impact on Rankings
When you have mobile-first indexing, Google ranks your ecommerce site based on its mobile version rather than its desktop version. Prioritizing it provides insight into how internet usage is shifting. A critical ranking factor in this process is page speed. In addition to increasing customer satisfaction, a speedier website lets Google know that it is mobile-friendly, which can raise the online store’s Google ranks.
Enhancing User Experience for Better Engagement
Metrics measuring user engagement are greatly impacted by mobile user experience. Reduced bounce rates, longer dwell times, and more views are the results of responsive design and responsive navigation.
To improve text accessibility on smaller displays, choose readable text sizes and fonts. Additionally, make input fields and forms simpler to reduce typing on the devices. Optimize screen features to prevent errors when users are engaging with an ecommerce site.
Monitoring and Improving Technical SEO Performance
Audits are essential for getting and enhancing your product pages. Insights for SEO let you know which pages are doing well and which require edits to have more results. Auditing helps to identify issues as they arise, obtaining the most impactful pages and drawing attention to more significant problems.
Think, what would occur if users visited one of your fruitful pages and were met with a 404 error code? You’ll lose countless visitors and conversions if you were using manual crawls because you wouldn’t know the page had a problem until the next crawl.
Google Search Console for Technical Insights
Besides checking to see if the pages are categorized or have Google Manual Actions against them, use Google Search Console to analyze how well your pages are running in comparison to expectations.
You’ll check the scannability and rendering status of any URL on the property using the URL inspection tool. The Core Web Vitals report can be used to assess the loading speed, responsiveness, and visual stability of an ecommerce site.
Regular SEO Audits
Begin with setting up adequate time for an SEO audit for all the data. Will you examine the whole website or particular product pages? Determine the scope upfront. Then, get analytics tools, such as Google Analytics, to examine historical user trends and data on keyword research. To find crawler issues, use just Google Search Console.
Tools for Running a Technical SEO Audit
For example, you may utilize Chrome DevTools to explore and diagnose problems on websites and make changes right away.
PageSpeed Insights helps you identify your UX strengths and areas for significant development by reporting on the quality of a page’s user experience on both desktop and mobile devices.
Common Technical Issues for Ecommerce Websites
High-resolution images that aren’t compressed can cause load times to increase; CSS and JavaScript files that slow down rendering can cause visible content to be delayed; and slow servers can cause an initial loading to be delayed, which can affect LCP. These are some common ecommerce website issues that you should consider for future improvements.
FAQ
What are the best practices for technical SEO for ecommerce?
With technical SEO for ecommerce, you could do a thorough audit of your configuration. Improve the speed at which pages load because most users dislike waiting. It makes sense to optimize a website for crawlers to increase visibility. Making the online store easy to navigate is crucial if you want to optimize the experience of users.
How does structured data improve search engine rankings?
Because data structuring in SEO for ecommerce follows the same rules for ecommerce websites with different platforms and setups, it helps standardize material on the web. This makes it possible for Google to select various components from every webpage and produce special, improved SERP features.
How can I prevent duplicate content issues on my ecommerce website?
Use canonical tags to identify which of the two pages contains duplicate content so that Google knows which is the original. Page-level meta tags that are positioned in the header are called canonical tags. They improve the page’s position in Google ranks.
Is SEO worth it for ecommerce?
SEO for ecommerce is the only marketing medium that may raise brand exposure, particularly if social media is not the main target demographic. You can reach more people by raising your organic traffic by relying on keyword research and search intent targeting than you might with sponsored advertising.





